INDIAN COAST GUARD RESCUES SEVEN CREW FROM A FLOODING BARGE OFF MUMBAI
INDIAN COAST GUARD RESCUES SEVEN CREW FROM A FLOODING BARGE OFF MUMBAI
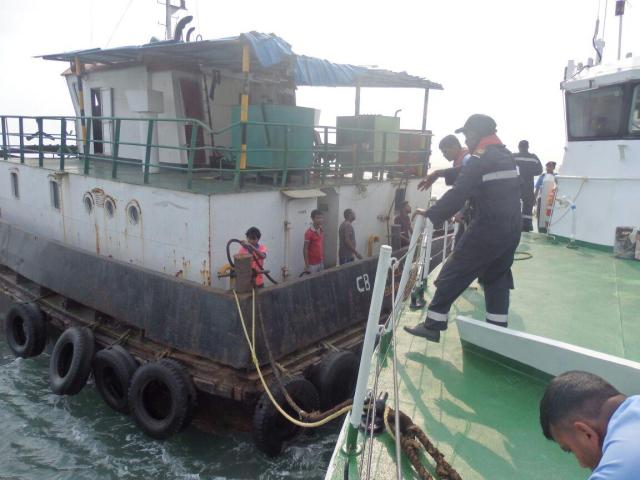

INDIAN COAST COAST GUARD RESCUES SEVEN CREW FROMA FLOODING
BARGE:
In a swift and well calibrated operation, Indian Coast
At about 1500 hrs on 29 Sep, a call was received at
Maritime Rescue Coordination Centre (MRCC) Mumbai from
VTS Mumbai regarding heavy flooding onboard an Indian
barge Ellysia 05 nm North-west of Colaba (Mumbai).
The vessel was on passage from Mumbai to Bhavnagar.
Immediately, Indian Coast Guard Ship C-154 was
diverted from patrol area to render assistance and by 1530
hrs, all the seven crew of the barge were safely evacuated.
Coast Guard team commenced the de-flooding of sea water
through two de-flooding pumps.
Another Coast Guard Ship Sankalp has also arrived in area to assist in de-
flooding.
Coast Guard has also mobilized Emergency Towing
Vessel from Mumbai Port for salvage operation. Till the last
report came in, all out efforts are in progress by Indian Coast
Guard to de-flood the barge Ellysia.
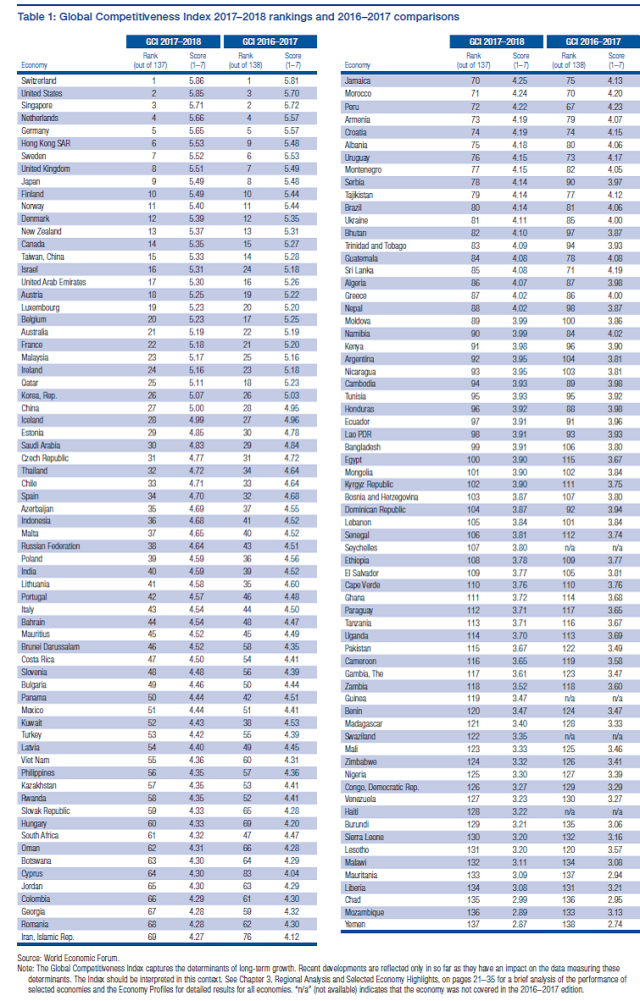
India slips a notch in Global Competitiveness Index : WEF
| According to the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) annual Global Competitiveness Index, India’s rank is down by a single position at 40th among 137 economies for the 2017-18 report, down from 39th position in 2016-17.
Switzerland remains the world’s most competitive economy, followed by the United States and Singapore. With Switzerland, the Netherlands and Germany stable on first, fourth and fifth spots, respectively, the only changes in the top five positions apply to the United States and Singapore, which swap second and third positions.
The GCI combines 114 indicators that capture concepts that matter for productivity and long-term prosperity. These indicators are grouped into 12 pillars : institutions, infrastructure, macroeconomic environment, health and primary education, higher education and training, goods market efficiency, labor market efficiency, financial market development, technological readiness, market size, business sophistication, and innovation. These pillars are in turn organized into three subindexes : basic requirements, efficiency enhancers, and innovation and sophistication factors.
Analysis of the Global Competitiveness Index (GCI) points to three main challenges and lessons that are relevant for economic progress, public-private collaboration, and policy action:
Ø First, 10 years after the crisis, the financial sector remains vulnerable- GCI indicators of bank soundness have not recovered to pre-crisis levels, new sources of vulnerability have emerged such as increasing private debt in emerging economies and the growth of non-regulated capital markets and governments have less bandwidth than they did 10 years ago to cope with another crisis. That is, ten years on from the global financial crisis, economies still remain at risk from further shock and are ill-prepared for the next wave of innovation and automation.
Ø Second, more countries are able to innovate, but they must do more to spread the benefits– Major emerging markets such as China, India, and Indonesia are becoming centers for innovation, catching up with advanced economies. However, they would benefit from accelerating progress in increasing the readiness of their people and firms to adopt new technology, which is necessary to widely spread innovation’s potential economic and societal benefits.
Ø Third, both labor market flexibility and worker protection are needed to ensure shared prosperity in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR) era- As globalization and rapid technological progress continue to test the ability of labor markets to reallocate workers between tasks and occupations, the GCI shows three parallel trends. First, measures of labor market flexibility are converging between advanced and emerging economies; second, more openness and economic integration has been accompanied by increased labor market flexibility; and third, greater labor market flexibility can coexist with protecting workers’ rights and reducing inequality. Together, these issues underscore the overall challenge for both advanced and emerging economies to reallocate factors of production to be flexible and responsive to technological trends while protecting people’s well-being during adjustment periods. Also, a decade of data illustrates the importance of balancing flexibility with protection in labour markets and why big hoped-for gains in productivity from innovation have remained elusive.
India’s ranking
For India (40th), the score improves across most pillars of competitiveness, particularly infrastructure (66th, up by two positions), higher education and training (75th, up by six positions), and technological readiness (107th, up by three positions), reflecting recent public investments in these areas. Performance also improved in Information and Communication Technology indicators, particularly Internet bandwidth per user, mobile phone and broadband subscriptions, and Internet access in schools. The quality of institutions has increased further, especially in terms of efficiency of public spending (20th), but the private sector still considers corruption to be the most problematic factor for doing business in India.
|
Musical Chair, Piyush Canceled GE Diesel Loco Deal
Not our views: researcher views and reviews
September29, 2017 (C) Ravinder Singh progressindia2015@gmail.com
Soon after the reshuffle of Ministries – World’s Most Weird Ideas are, like Maggi 2 Minute Instant Noodles, thrust upon India without any question asked or undergoing ‘Established Planning Processes.’ Foot Over Bridge stampede exposed Railways Gross Failure in serving Consumers – 10 Mumbai Commuters die daily – will get Bullet Train.
Our experts Are 100X More Dangerous to Indian Economy.
India not emerged out of NDA-I Irrational – River Linking; No Multipurpose Dam; Jatropha; Oil & Gas Exploration; Opening Tax Heaven Routes for FDI; Repeal of FERA & Land Ceiling; Banks funding 100% of Project cost than 40% to 66% for Large & SMEs Companies; Company Taking Loan at Low Cost then diverting to new company or project.
Piyush, Prabhu & Gadkari are least qualified to even think of Development Progress are – come up with Weird Ideas and without any details, study, would go ahead with their execution, are being rotated than shunted out of government. IR traffic growth is negative, Critical Projects are Stalled – nonviable projects are Pushed largely in 2-3 states that may cost over Rs.15,00,000 Cr, Load factor of power sector has declined to around 50%, worst of all – Rs.15,00,000 Cr are required for 45,000 km NHAI projects – this doesn’t account for State Road Projects & their maintenance.
Then ‘Suddenly On 21st’ Gadkari would announce 100% Electric Mobility [Automobiles] by 2030 –India Produced 25m Automobiles FY17, 400m Automobiles are to be Junked.
Next Piyush on 27th announced 100% electrification of Railway Network. Cancelled the Diesel Loco deal. As per his own estimate – Railways to save Rs.1,00,000 Cr in 10 years – half of it is Taxes – Saving of Rs.5,000 Cr a year is likely saving but would need Rs.5,00,000 Cr Investment on Electrification – Power Generation, Transmission & 6000 New Electric Locos, 1% in saving Energy Cost – Electrification O&M Cost 5 times more.
Diesel Locos Emit 70% Less CO2 Than Electric Locos.
Centre seeks 100% electric vehicles by 2030 – September21, 2017
Government will go ahead with its plan to have 100% electric mobility by 2030, road transport and highways minister Nitin Gadkari said on Wednesday. He said Niti Aayog will send the policy for Cabinet approval soon. Gadkari had a long meeting with Niti Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant on Wednesday on the electric vehicle policy. Sources said the highway minister has supported the policy, which Niti Aayog has prepared. Two ministries transport and heavy industries and Niti Aayog have a major role to play in preparing the policy.
Though government officials were tight lipped about the details of the policy, they said there will be enabling provision to accelerate manufacturing of electric vehicles. These would include government incentive as well. They added the government has already pushed the need for mass scale production of lithium-ion batteries, which is crucial for the roll out of the mission.
Apr-Jul Trade Deficit Doubled from $27b to $51.5b – Economy in Deep Dive.
Ravinder Singh, Inventor & Consultant, INNOVATIVE TECHNOLOGIES AND PROJECTS
Y-77, Hauz Khas, ND -110016, India. Ph: 091- 9871056471, 9718280435, 9650421857
Ravinder Singh* is a WIPO awarded inventor specializing in Power, Transportation,
Smart Cities, Water, Energy Saving, Agriculture, Manufacturing, Technologies and Projects